Traefik. Concept term explanation
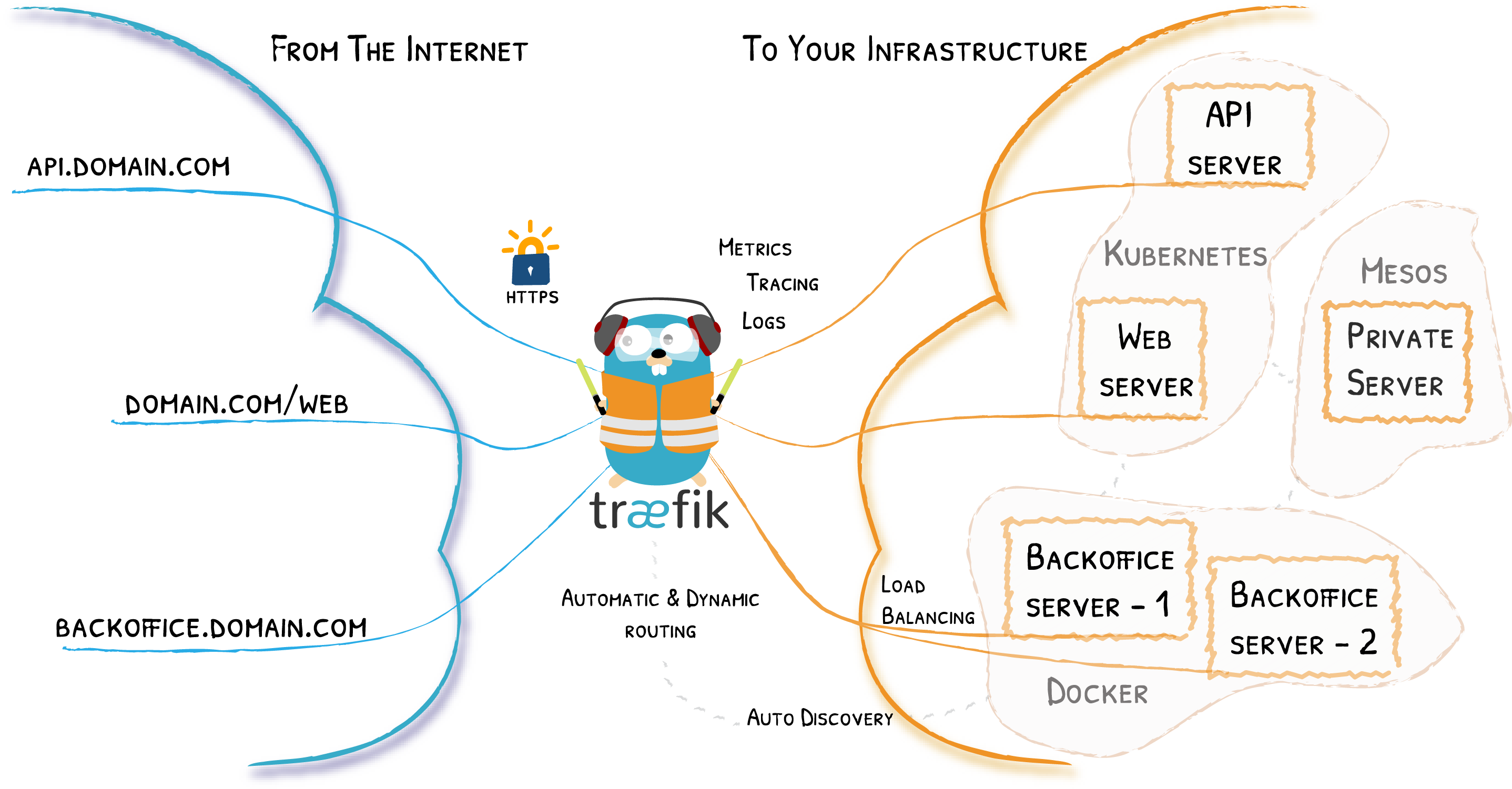
Traefik is an open-source Edge Router that makes publishing your services a fun and easy experience. It receives requests on behalf of your system and finds out which components are responsible for handling them.
Traefik perfectly bound with Docker engine, just attach labels to your containers and let Traefik do the rest!
But if are new in Traefik you will have some difficulties to understand what does it mean all this specific words. In here I would like to explain the basic definition of them. Let’s start.
Provider
Traefik is able to use your cluster API to discover the services and read the attached information. In Traefik, these connectors are called Providers because they provide the configuration to Traefik. The idea is that Traefik will query the providers’ API in order to find relevant information about routing, and each time Traefik detects a change, it dynamically updates the routes.
To define a connection with docker add next parameter to a traefik command:
--providers.docker=true
EntryPoint
EntryPoints are the network entry points into Traefik. They define the port which will receive the requests (whether HTTP or TCP). EntryPoints are part of the static configuration. You can define them using a toml file, CLI arguments, or a key-value store.
For example
--entryPoints.web.address=:80
--entryPoints.websecure.address=:443
- Two entrypoints are defined: one called
web, and the other calledwebsecure. weblistens on port 80, andwebsecureon port 443.
Router
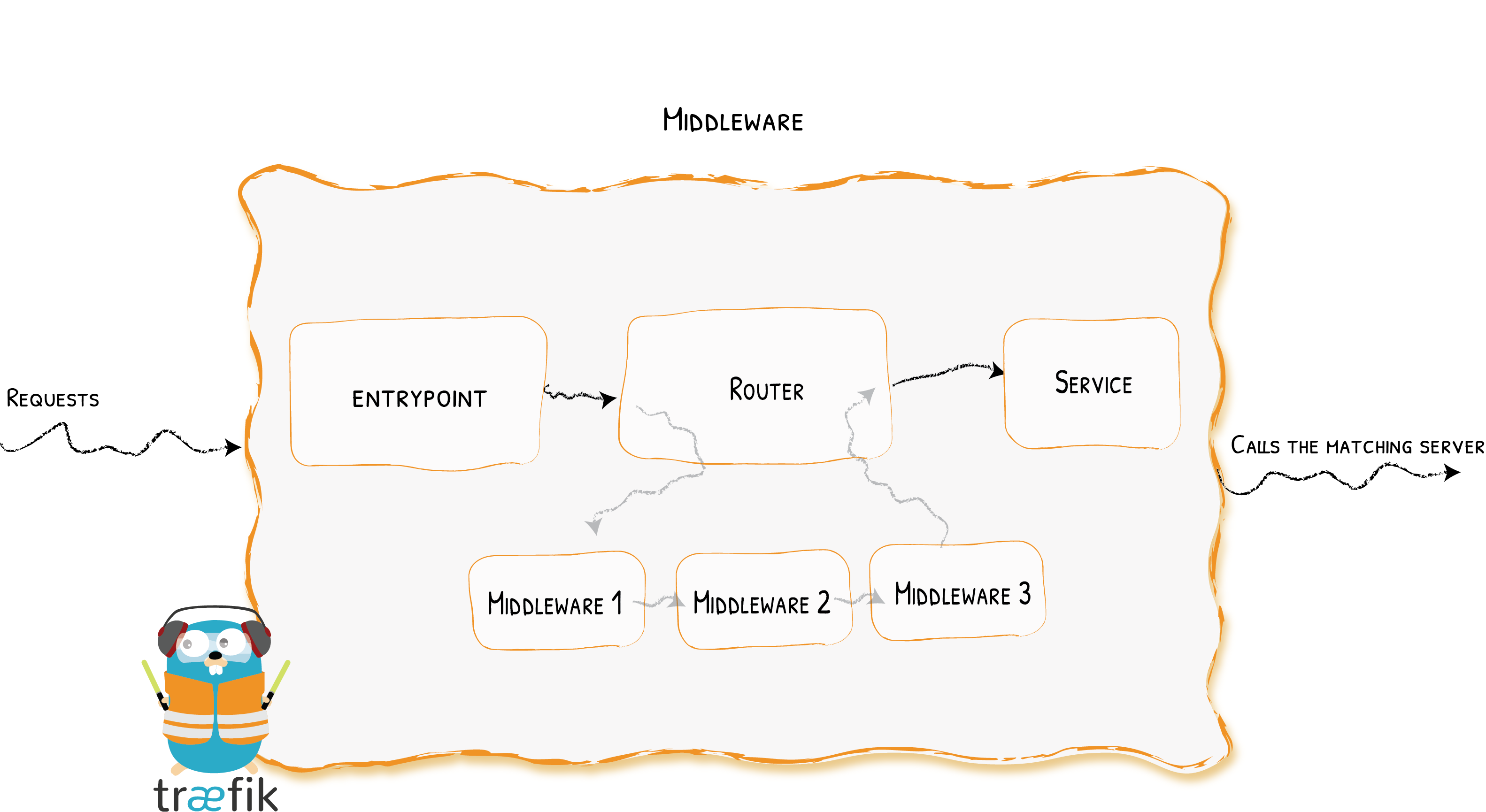
The main function is a connecting Requests from EntryPoint to Services.
Router is in charge of connecting incoming requests to the services that can handle them. In the process, routers may use pieces of middleware to update the request, or act before forwarding the request to the service.
Configuration example
--traefik.http.routers.whoami.entrypoints=web
--traefik.http.routers.whoami.rule=Host(`whoami.localhost`)
- The router has name
whoamiand will get requests fromwebentrypoint. - Defined rule
Host('whoami.localhost')will allow only requests for domain ‘whoami.localhost’
Rule
Rules are a part of Router. In detail it is a set of matchers configured with values, that determine if a particular request matches specific criteria. If the rule is verified, the router becomes active, calls middlewares, and then forwards the request to the service.
rule = "Host(`traefik.io`) || (Host(`containo.us`) && Path(`/traefik`))"
Middleware
Middleware needs for tweaking the Request. Attached to the routers, pieces of middleware are a means of tweaking the requests before they are sent to your service (or before the answer from the services are sent to the clients).
There are several available middleware, some can modify the request, the headers, some are in charge of redirections, some add authentication, and so on. The middlewares will take effect only if the route rule matches, and before forwarding the request to the service.
Example of creating and attaching a middleware (add BasicAuth to the Service):
--traefik.http.routers.api.rule=Host(`traefik.example.com`)
--traefik.http.routers.api.service=api@internal
--traefik.http.routers.api.middlewares=auth
--traefik.http.middlewares.auth.basicauth.users=user:$$apr1$$mW/l73Bf$$Wsprk23sa5.QbLdY3sak7hf0"
- Firs of all we create a route
apiwith rule that will pass traffic only fortraefik.example.comdomain - We attach an internal traefik service to this route -
api@internal - Also we attach a middleware
auththat we explain in the next row - The new middleware has name
auth. It’s a BasicAuth middleware. It To create a user:password pair, the following command can be used:# echo $(htpasswd -nb user password) | sed -e s/\\$/\\$\\$/g
Service
Services are responsible for configuring how to reach the actual services that will eventually handle the incoming requests.
Each request must eventually be handled by a service, which is why each router definition should include a service target, which is basically where the request will be passed along to.
To define a usage of the specific port
--traefik.http.services.myapp.loadbalancer.server.port=8082
- The service
myappwill income requests between servers that listen on port8082
In the next post will show you how to use Traefik with Docker containers.
Additional information
- Official Documentation - the start point to know more about Traefik
- Traefik 2.0 & Docker 101 - tips & tricks the Documentation Doesn’t Tell You